 North Korea Increases Aid to Russia, Mos... Tue Nov 19, 2024 12:29 | Marko Marjanovi? North Korea Increases Aid to Russia, Mos... Tue Nov 19, 2024 12:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 Trump Assembles a War Cabinet Sat Nov 16, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi? Trump Assembles a War Cabinet Sat Nov 16, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 Slavgrinder Ramps Up Into Overdrive Tue Nov 12, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi? Slavgrinder Ramps Up Into Overdrive Tue Nov 12, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 ?Existential? Culling to Continue on Com... Mon Nov 11, 2024 10:28 | Marko Marjanovi? ?Existential? Culling to Continue on Com... Mon Nov 11, 2024 10:28 | Marko Marjanovi?
 US to Deploy Military Contractors to Ukr... Sun Nov 10, 2024 02:37 | Field Empty US to Deploy Military Contractors to Ukr... Sun Nov 10, 2024 02:37 | Field Empty Anti-Empire >>
Indymedia Ireland is a volunteer-run non-commercial open publishing website for local and international news, opinion & analysis, press releases and events. Its main objective is to enable the public to participate in reporting and analysis of the news and other important events and aspects of our daily lives and thereby give a voice to people.
 Fraud and mismanagement at University College Cork Thu Aug 28, 2025 18:30 | Calli Morganite Fraud and mismanagement at University College Cork Thu Aug 28, 2025 18:30 | Calli Morganite
UCC has paid huge sums to a criminal professor
This story is not for republication. I bear responsibility for the things I write. I have read the guidelines and understand that I must not write anything untrue, and I won't.
This is a public interest story about a complete failure of governance and management at UCC.
 Deliberate Design Flaw In ChatGPT-5 Sun Aug 17, 2025 08:04 | Mind Agent Deliberate Design Flaw In ChatGPT-5 Sun Aug 17, 2025 08:04 | Mind Agent
Socratic Dialog Between ChatGPT-5 and Mind Agent Reveals Fatal and Deliberate 'Design by Construction' Flaw
This design flaw in ChatGPT-5's default epistemic mode subverts what the much touted ChatGPT-5 can do... so long as the flaw is not tickled, any usage should be fine---The epistemological question is: how would anyone in the public, includes you reading this (since no one is all knowing), in an unfamiliar domain know whether or not the flaw has been tickled when seeking information or understanding of a domain without prior knowledge of that domain???!
This analysis is a pretty unique and significant contribution to the space of empirical evaluation of LLMs that exist in AI public world... at least thus far, as far as I am aware! For what it's worth--as if anyone in the ChatGPT universe cares as they pile up on using the "PhD level scholar in your pocket".
According to GPT-5, and according to my tests, this flaw exists in all LLMs... What is revealing is the deduction GPT-5 made: Why ?design choice? starts looking like ?deliberate flaw?.
People are paying $200 a month to not just ChatGPT, but all major LLMs have similar Pro pricing! I bet they, like the normal user of free ChatGPT, stay in LLM's default mode where the flaw manifests itself. As it did in this evaluation.
 AI Reach: Gemini Reasoning Question of God Sat Aug 02, 2025 20:00 | Mind Agent AI Reach: Gemini Reasoning Question of God Sat Aug 02, 2025 20:00 | Mind Agent
Evaluating Semantic Reasoning Capability of AI Chatbot on Ontologically Deep Abstract (bias neutral) Thought
I have been evaluating AI Chatbot agents for their epistemic limits over the past two months, and have tested all major AI Agents, ChatGPT, Grok, Claude, Perplexity, and DeepSeek, for their epistemic limits and their negative impact as information gate-keepers.... Today I decided to test for how AI could be the boon for humanity in other positive areas, such as in completely abstract realms, such as metaphysical thought. Meaning, I wanted to test the LLMs for Positives beyond what most researchers benchmark these for, or have expressed in the approx. 2500 Turing tests in Humanity?s Last Exam.. And I chose as my first candidate, Google DeepMind's Gemini as I had not evaluated it before on anything.
 Israeli Human Rights Group B'Tselem finally Admits It is Genocide releasing Our Genocide report Fri Aug 01, 2025 23:54 | 1 of indy Israeli Human Rights Group B'Tselem finally Admits It is Genocide releasing Our Genocide report Fri Aug 01, 2025 23:54 | 1 of indy
We have all known it for over 2 years that it is a genocide in Gaza
Israeli human rights group B'Tselem has finally admitted what everyone else outside Israel has known for two years is that the Israeli state is carrying out a genocide in Gaza
Western governments like the USA are complicit in it as they have been supplying the huge bombs and missiles used by Israel and dropped on innocent civilians in Gaza. One phone call from the USA regime could have ended it at any point. However many other countries are complicity with their tacit approval and neighboring Arab countries have been pretty spinless too in their support
With the release of this report titled: Our Genocide -there is a good chance this will make it okay for more people within Israel itself to speak out and do something about it despite the fact that many there are actually in support of the Gaza
 China?s CITY WIDE CASH SEIZURES Begin ? ATMs Frozen, Digital Yuan FORCED Overnight Wed Jul 30, 2025 21:40 | 1 of indy China?s CITY WIDE CASH SEIZURES Begin ? ATMs Frozen, Digital Yuan FORCED Overnight Wed Jul 30, 2025 21:40 | 1 of indy
This story is unverified but it is very instructive of what will happen when cash is removed
THIS STORY IS UNVERIFIED BUT PLEASE WATCH THE VIDEO OR READ THE TRANSCRIPT AS IT GIVES AN VERY GOOD IDEA OF WHAT A CASHLESS SOCIETY WILL LOOK LIKE. And it ain't pretty
A single video report has come out of China claiming China's biggest cities are now cashless, not by choice, but by force. The report goes on to claim ATMs have gone dark, vaults are being emptied. And overnight (July 20 into 21), the digital yuan is the only currency allowed. The Saker >>
Interested in maladministration. Estd. 2005
 RTEs Sarah McInerney ? Fianna Fail?supporter? Anthony RTEs Sarah McInerney ? Fianna Fail?supporter? Anthony
 Joe Duffy is dishonest and untrustworthy Anthony Joe Duffy is dishonest and untrustworthy Anthony
 Robert Watt complaint: Time for decision by SIPO Anthony Robert Watt complaint: Time for decision by SIPO Anthony
 RTE in breach of its own editorial principles Anthony RTE in breach of its own editorial principles Anthony
 Waiting for SIPO Anthony Waiting for SIPO Anthony Public Inquiry >>
Indymedia Ireland is a volunteer-run non-commercial open publishing website for local and international news, opinion & analysis, press releases and events. Its main objective is to enable the public to participate in reporting and analysis of the news and other important events and aspects of our daily lives and thereby give a voice to people.
 Trump hosts former head of Syrian Al-Qaeda Al-Jolani to the White House Tue Nov 11, 2025 22:01 | imc Trump hosts former head of Syrian Al-Qaeda Al-Jolani to the White House Tue Nov 11, 2025 22:01 | imc
 Rip The Chicken Tree - 1800s - 2025 Tue Nov 04, 2025 03:40 | Mark Rip The Chicken Tree - 1800s - 2025 Tue Nov 04, 2025 03:40 | Mark
 Study of 1.7 Million Children: Heart Damage Only Found in Covid-Vaxxed Kids Sat Nov 01, 2025 00:44 | imc Study of 1.7 Million Children: Heart Damage Only Found in Covid-Vaxxed Kids Sat Nov 01, 2025 00:44 | imc
 The Golden Haro Fri Oct 31, 2025 12:39 | Paul Ryan The Golden Haro Fri Oct 31, 2025 12:39 | Paul Ryan
 Top Scientists Confirm Covid Shots Cause Heart Attacks in Children Sun Oct 05, 2025 21:31 | imc Top Scientists Confirm Covid Shots Cause Heart Attacks in Children Sun Oct 05, 2025 21:31 | imc Human Rights in Ireland >>
|
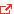
Cuba Flies Lone Flag for Sustainability
 international |
environment |
other press international |
environment |
other press
 Thursday October 11, 2007 23:10 Thursday October 11, 2007 23:10 by Tech1.0 by Tech1.0

According to a new study on ecological sustainablity published in New Scientist, Cuba is showing the way on life in a post-oil world.
(from last week's New Scientist - I'm publishing this in the inter-national public interest...)
"We don’t need environmental evangelicals to tell us that sustainable development is a good idea. Yet, if that is our goal, we are heading in the wrong direction - with the exception of Cuba. So says the first study to examine the ecological impact of changing lifestyles around the globe.
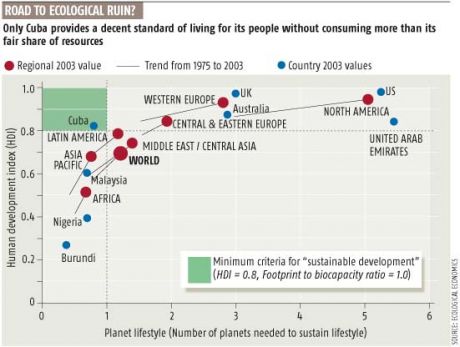 We don’t need environmental evangelicals to tell us that sustainable development is a good idea. Yet, if that is our goal, we are heading in the wrong direction - with the exception of Cuba. So says the first study to examine the ecological impact of changing lifestyles around the globe.
An international team led by Mathis Wackernagel of the Global Footprint Network looked at how the living conditions and ecological footprints of 93 nations have changed in the last 30 years.
They used the ecological footprint (EF) index, a tool devised in 1993 by Wackernagel and William Rees, his PhD supervisor at the University of British Columbia, Canada. EF quantifies the area of land required to provide the infrastructure used by a person or a nation, the food and goods they consume, and to reabsorb the waste they produce, using available technology. This value can then be compared with the resources that are actually available to people on a regional or global scale. EF has become a popular index, and was used recently, for example, by conservation group WWF to calculate that two more planets would be needed to support everyone in the world in the manner of the average UK citizen.
However, rather than just measure consumption, Wackernagel and his colleagues wanted to measure how close countries are to developing in a sustainable way. The problem is that “sustainability” is an elusive concept. “Nobody dares to say what it actually means,” Wackernagel told New Scientist. “We believe we provided a robust measurement.”
For each nation with reliable data, they calculated how many planets would be needed to support the global population if everybody adopted that nation’s lifestyle as it was in 1978, and in 2003. They then expressed each figure as an Earth-equivalent ratio (EER) and plotted each value against the nation’s corresponding UN Human Development Index. The index is a score of between 0 and 1, and is a function of a country’s average life expectancy, adult literacy, level of schooling and per capita GDP.
To develop sustainably, the researchers assume a country must have an HDI of at least 0.8 and a maximum EER of 1 (see Diagram). A lower HDI would mean a nation is not developing adequately, while a higher EER means it is gobbling up too many resources.
By looking at each country’s historical trajectory, a clear pattern emerges. People everywhere have a better lifestyle, but their footprint is growing at a rate proportional to their wealth. Developed countries in particular have done very little to reduce their impact. Only one nation, Cuba, is developing sustainably, and probably not for long (Ecological Economics, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.08.017). “Cubans have high life expectancy and literacy, and were forced into a smaller footprint because of the oil embargo,” says Wackernagel. “But they are now economically more successful, and will tend to use more resources.”
Critics point out that EF calculations do not take into account issues such as pollution from certain toxic chemicals, and place too much reliance on others, such as carbon footprints, which may be alleviated by the invention of new technologies. Even so, “it’s a broad indicator of the direction things are moving, and it’s an excellent tool for communicating to the public and decision makers,” says Jan Vernon, who reviewed the validity of EF for the UK government.
The study, therefore, carries a credible message: we have all moved away from sustainability, and the world has entered ecological overshoot. “We have not taken sustainable development seriously,” Wackernagel concludes.
"
New Scientist link
http://tinyurl.com/3bdju5
http://www.footprintnetwork.org/index.php
http://www.wwf.org.uk/researcher/issues/footprint/index.asp
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_Development_Index
Measuring sustainable development — Nation by nation (sciencedirect)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.08.017
and for more on this theme check out the fascinating documentary below,
The Power of Community: How Cuba Survived Peak Oil
http://www.powerofcommunity.org/cm/index.php
http://globalpublicmedia.com/articles/657
|
 international |
environment |
other press
international |
environment |
other press
 Thursday October 11, 2007 23:10
Thursday October 11, 2007 23:10 by Tech1.0
by Tech1.0
























 printable version
printable version

 Digg this
Digg this del.icio.us
del.icio.us Furl
Furl Reddit
Reddit Technorati
Technorati Facebook
Facebook Gab
Gab Twitter
Twitter
View Comments Titles Only
save preference
Comments (2 of 2)
Jump To Comment: 1 2Of course to qualify this it must be stated that one of the reasons that Cubans may not leave such an ecological footprint is because they cannot afford- to a large degree- travel within the island and certainly not internationally. The equivalent of 20 US dollars a month leaves little for leisure travel and many recreational activites that the developed world can afford and that can harm the environment. Perhaps this is a factor in them 'showing the way'.
Eamon, I'm sure the constraining of consumption is a factor. But as Monbiot points out in Heat, ( http://www.monbiot.com/archives/2006/11/07/heat/ ) air travel will need to be constrained practically completely anyway, as there's no way it can continue as it is.
Cuba is an example of an efficient delivery of a wide range of public services within what the Earth can take. Due, largely, to its unfortunate history it is not an example in terms of democratically reaching a sustainable solution. But that doesn't stop us from examining how such a human-development vs consumption result can be generated for the Earth as a whole.
Personally I think it shows a possible solution although ideally coupled with more participatory mechanisms....
Protecting the Environment in a Participatory Economy
http://www.greens.org/s-r/34/34-18.html
"....The crucial difference between participatory planning and market economies in this regard is that the participatory planning procedure generates quantitative estimates of the costs and benefits of pollution while markets do not. Consequently, even “good faith” efforts to internalize the cost of pollution through taxes or permits in market economies are “flying blind,” and opportunities for “bad faith” intervention are ever present. Estimates from “contingent valuation surveys” and “hedonic regression studies” are less accurate than the indicative prices for pollutants that are generated automatically by the participatory planning procedure. Moreover, because everyone knows estimates based on surveys and studies are unreliable, it is possible for interested parties in market economies to challenge estimates they find inconvenient. Interested parties frequently finance alternative surveys and studies that arrive at predictably different conclusions regarding the damage from pollution and benefits from environmental preservation.
Since, unlike participatory planning, market systems generate no “objective” estimates that could serve as arbiters, debates over the size of pollution taxes in market economies invariably devolve into a cacophony of “he says, she says.” The participatory planning procedure described above, on the other hand, provides credible estimates of the damage done by pollution because the above procedure makes it in the interest of pollution victims to reveal the extent of the damage they suffer truthfully as a byproduct of simply participating in the planning procedure. ..."